文章来源于互联网:Mercedes to Add ChatGPT to its Infotainment System

Mercedes is set to revolutionize the way drivers and passengers interact with their cars.
The automaker announced plans to integrate ChatGPT, an advanced conversational AI developed by OpenAI, into its infotainment systems.
The integration is part of a beta program launching from June 16, 2023, giving Mercedes customers in the U.S. a chance to experience more engaging and personalized interactions with their vehicles.
A New Era of Interactive Driving
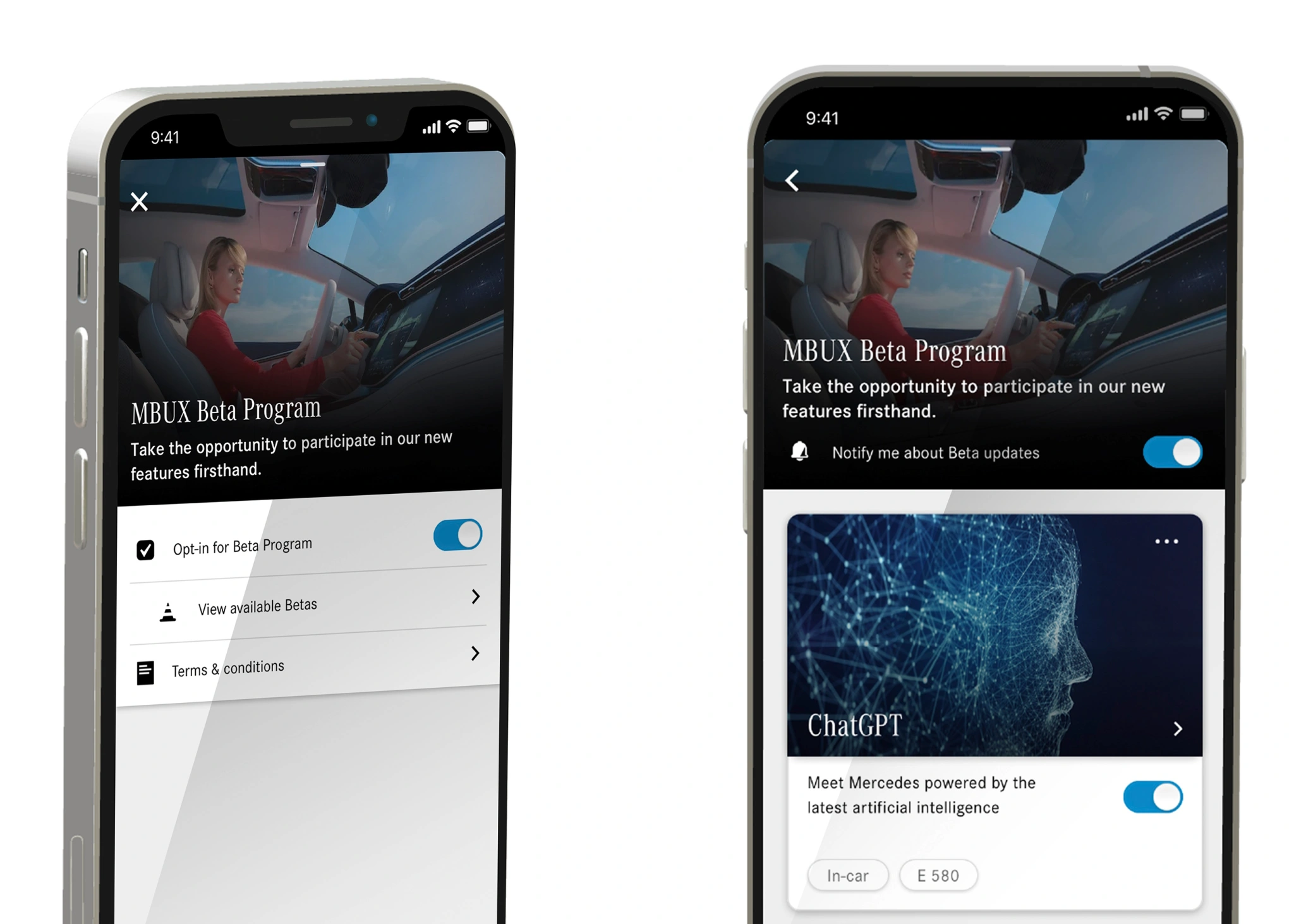
This innovative development allows Mercedes owners to upgrade their existing MBUX (Mercedes-Benz User Experience) systems with ChatGPT’s functionalities.
A simple voice command, “Hey Mercedes, I want to join the beta program,” will allow the users to enjoy this new addition, enhancing their in-car interactions.
ChatGPT is designed to mimic human-like conversation across diverse subjects. While its capabilities include content synthesis, code writing, and even creative tasks like crafting wedding vows, its role in the car environment remains to be explored fully.
Mercedes believes that ChatGPT’s conversational skills will add value to the driving experience.
“Users will experience a voice assistant that not only accepts natural voice commands but can also conduct conversations,” the automaker stated in a press release.
This feature can provide drivers with comprehensive answers to complex questions, assist with destination details, or even suggest new dinner recipes, all while ensuring their focus remains on the road.
While this integration promises to make car journeys more interesting and engaging, some concerns arise.
Are these wide-ranging functionalities necessary for drivers or passengers? What kind of interactions do users actually prefer while on the move? The answers to these questions are yet to unfold.
Mercedes’ choice to partner with ChatGPT, a third-party service, is a strategic decision to elevate its voice interface service.
However, with this enhancement comes the responsibility of managing user data.
Although the conversations between users and the voice interface are stored in the Mercedes-Benz Intelligent Cloud and anonymized, privacy concerns are still relevant.
Mercedes emphasizes that this data collection is crucial for understanding user behavior, shaping the rollout strategy, and improving the voice assistant across markets and languages.
While the feature’s practicality and privacy implications are subjects of ongoing discussion, one thing is clear: this beta program propels Mercedes towards a future where cars are not just machines, but conversational companions.
Time will tell how this new feature impacts the everyday driving experience of Mercedes owners.
































































评论